CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE)
The CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE) is an international collaboration between more than 300 partners that seeks to mobilize global resources in maize research and development to achieve a greater strategic impact on maize-based farming systems in Africa, Latin America and South Asia.
Led by the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT), with the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) as its main CGIAR partner, MAIZE focuses on increasing maize production for the 900 million poor consumers for whom maize is a staple food in Africa, Latin America and South Asia. MAIZE’s overarching goal is to double maize productivity and increase incomes and livelihood opportunities from sustainable maize-based farming systems.
MAIZE receives funding support from CGIAR Trust Fund contributors.
MAIZE Flagship Projects (FPs) and Cluster of Activities
FP1: Enhancing MAIZE’s R4D strategy for impact
• Foresight and targeting of R4D strategies
• Learning from M&E, adoption and impacts
• Enhancing gender and social inclusiveness
• Value chain analysis
FP2: Novel diversity and tools for improving genetic gains
• Informatics, database management and decision support tools
• Development of enabling tools for germplasm improvement
• Unlocking genetic diversity through trait exploration and gene discovery
• Pre-breeding: development of germplasm resources
FP3: Stress-tolerant and nutritious maize
• Climate resilient maize with abiotic and biotic stress tolerance
• Tackling emerging trans-boundary disease/pest challenges
• Nutritional quality and end-use traits in elite genetic backgrounds
• Precision phenotyping and mechanization of breeding operations
• Seed production research and recommendations
• Stronger maize seed systems
FP4: Sustainable intensification of maize-based systems
• Multi-scale farming system framework to better integrate and enhance adoption of sustainable intensification options
• Participatory adoption and integration of technological components
• Development and field-testing of crop management technologies
• Partnership and collaborations models for scaling
New association formed to support smallholder native maize farmers in Mexico
 Capacity development
Capacity development
ProMaíz Nativo will promote small-scale landrace maize farmers through certification and fair market access.
Call for Nominees for the 2019 Maize Youth Innovators Awards – Latin America
 Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
Open to young women and men under 35 who are implementing innovations in Latin American maize-based agri-food systems.
Are high land rental costs pricing African youth out of agriculture?
 Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
Rural land grows scarce as populations rise and more youth farm for their livelihoods.
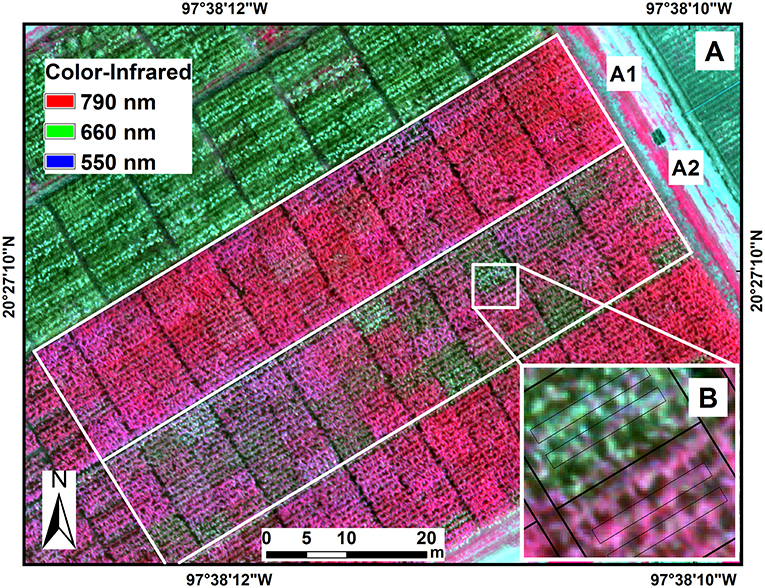
Bird’s-eye view
 Innovations
Innovations
Multispectral and thermal images taken by cameras on unmanned aerial vehicles are helping researchers to monitor the resistance of maize to tar spot complex and other foliar diseases.
Research, innovation, partnerships, impact
 Innovations
Innovations
Knowledge share fair highlights CGIAR contributions to the Ethiopian agriculture sector.
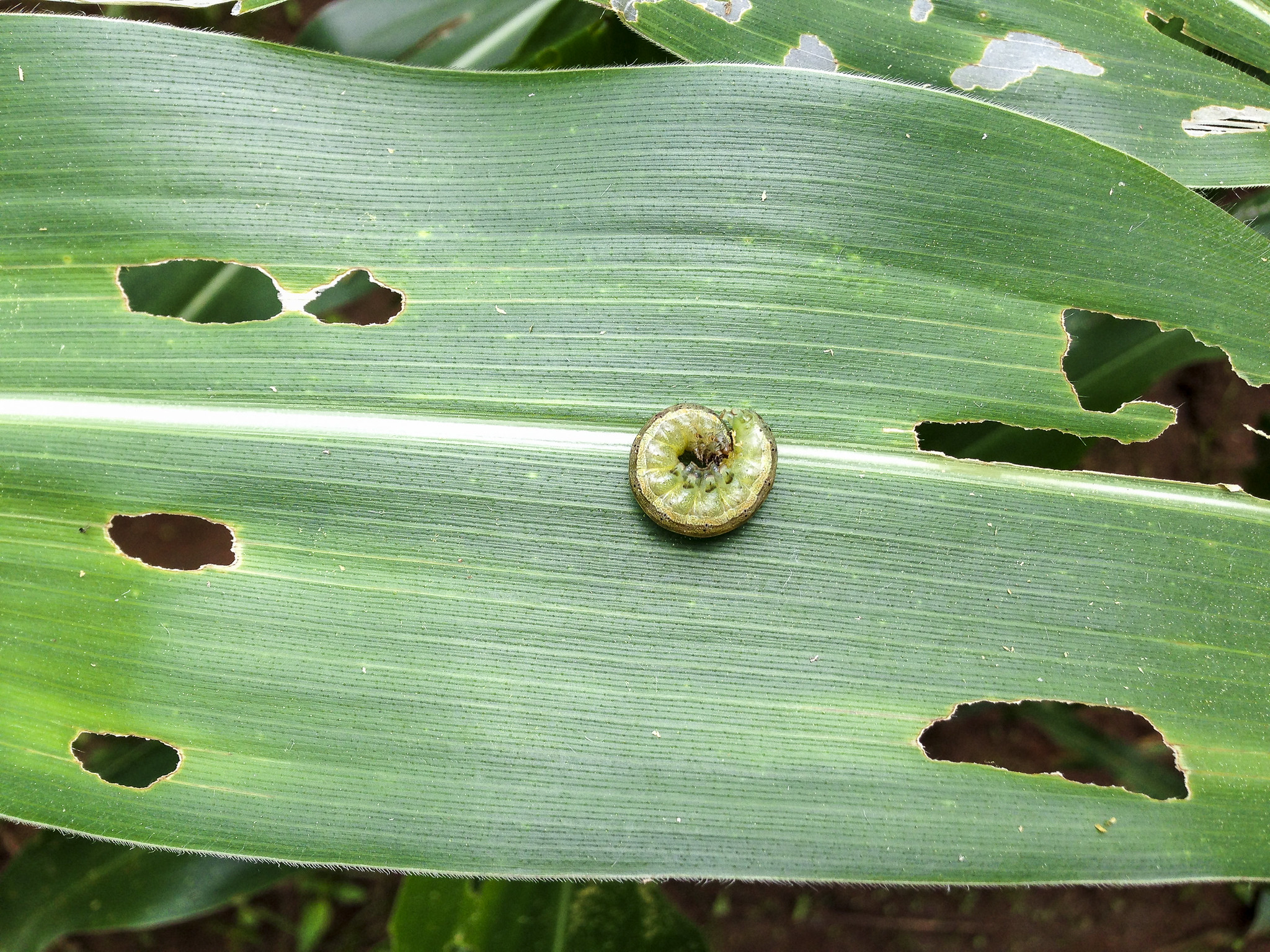
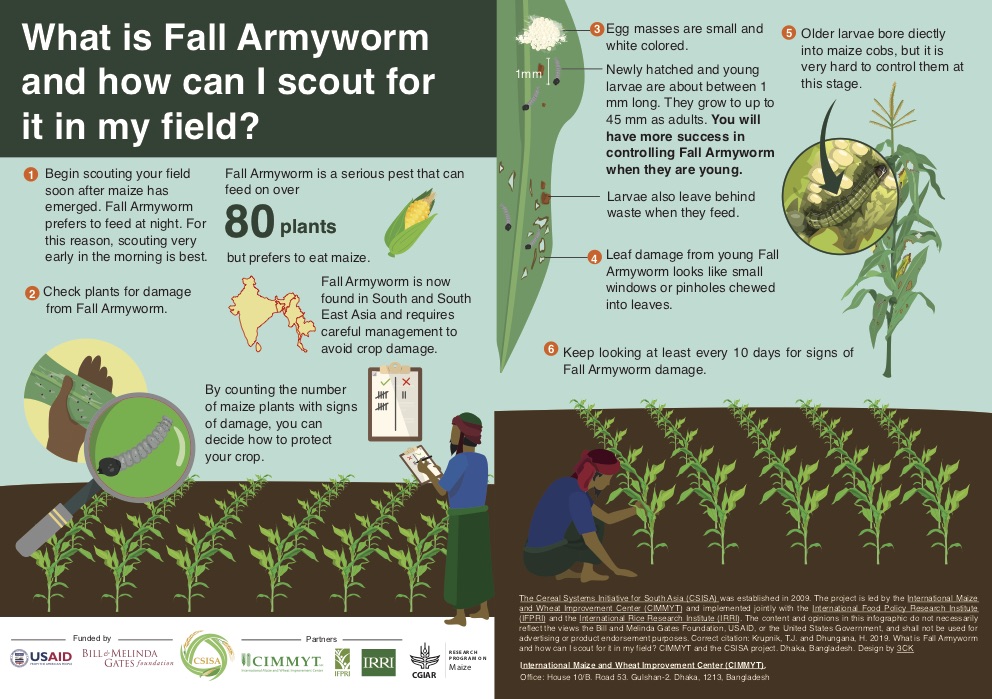
The fall armyworm, explained
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
A series of infographics shows farmers in Bangladesh the threat of fall armyworm, how to identify it in the fields and what to do in case of damage.
Shifting to a demand-led maize improvement agenda
 Climate adaptation and mitigation
Climate adaptation and mitigation
In annual meeting, STMA project partners build on the successes of research in combatting drought, heat, pests and disease.
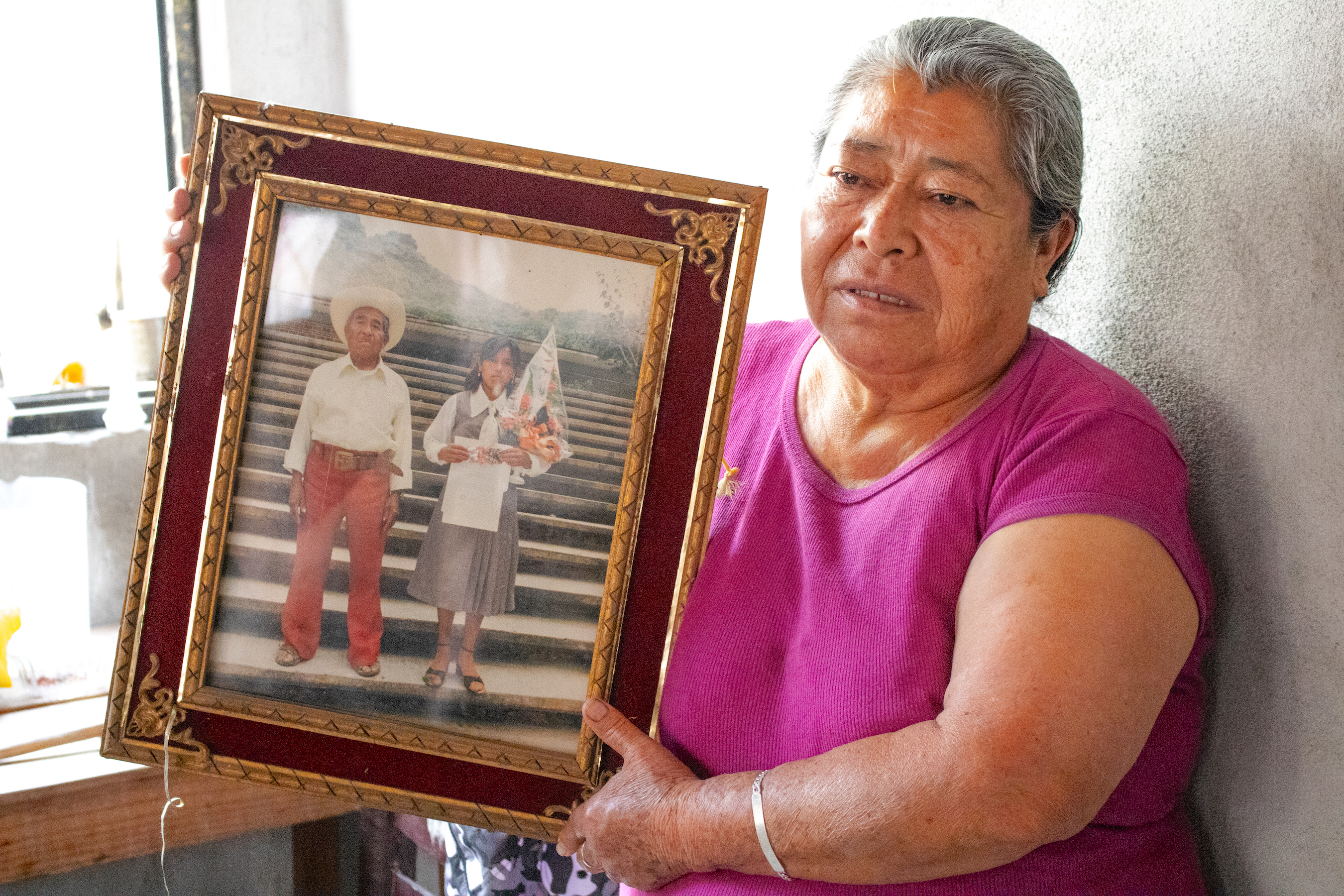
Tracing maize landraces, 50 years later
 Environmental health and biodiversity
Environmental health and biodiversity
Scientists track down the families in Morelos, Mexico, who donated maize landraces to CIMMYT in 1966-67. Would they still be cultivating them?
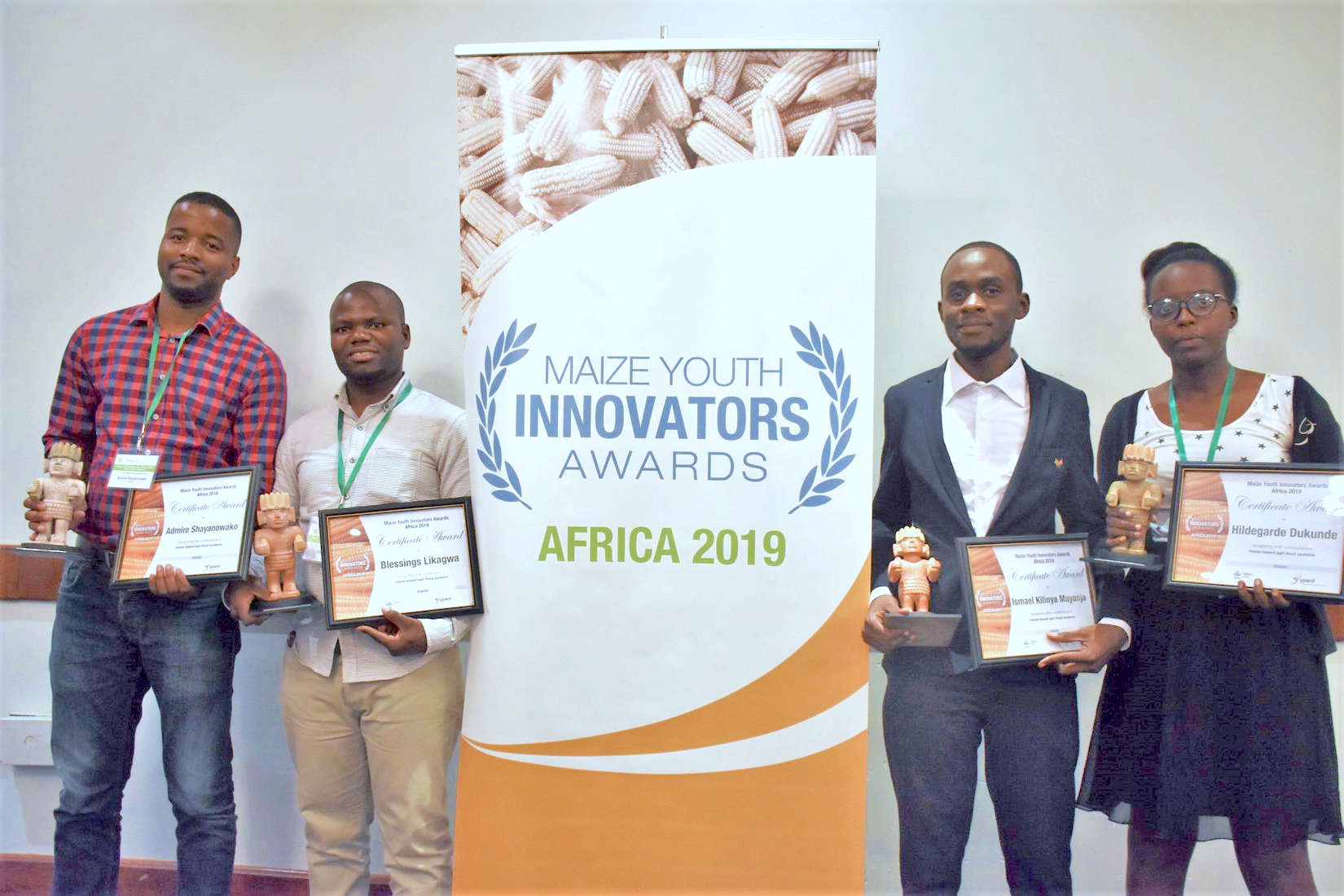
Winners of 2019 MAIZE Youth Innovators Awards – Africa announced
 Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
Gender equality, youth and social inclusion
The five young awardees are advancing change, innovation and research in their communities.
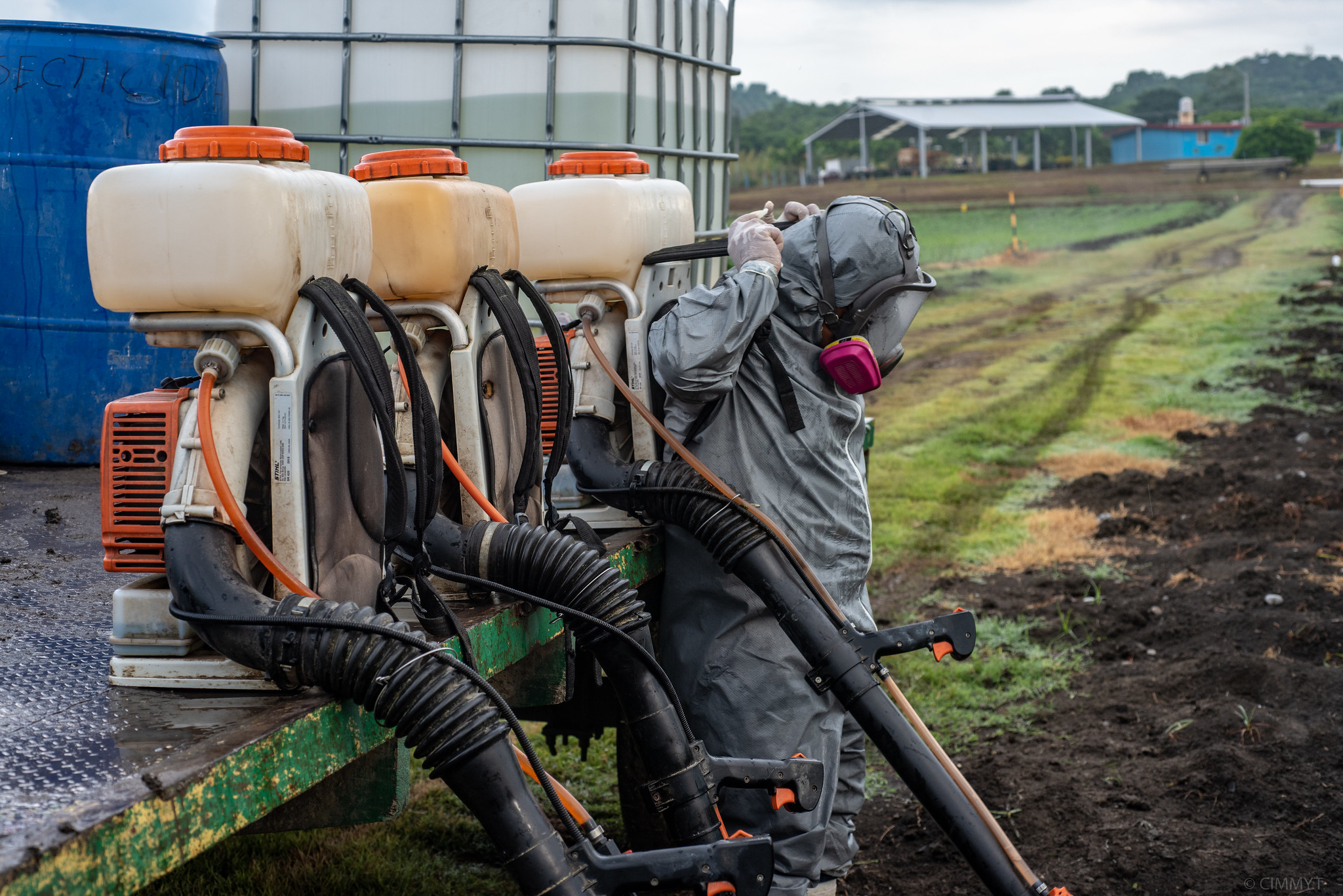
New study identifies best agronomic practices to reduce fall armyworm damage
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
Good weed management, conservation agriculture, and use of manure and compost are recommended to help control fall armyworm in Africa.
CIMMYT and UAS-Bangalore to establish a maize doubled haploid facility in Karnataka, India
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
Occupying 12 acres of land, the facility is expected to produce at least 30,000 DH lines a year.
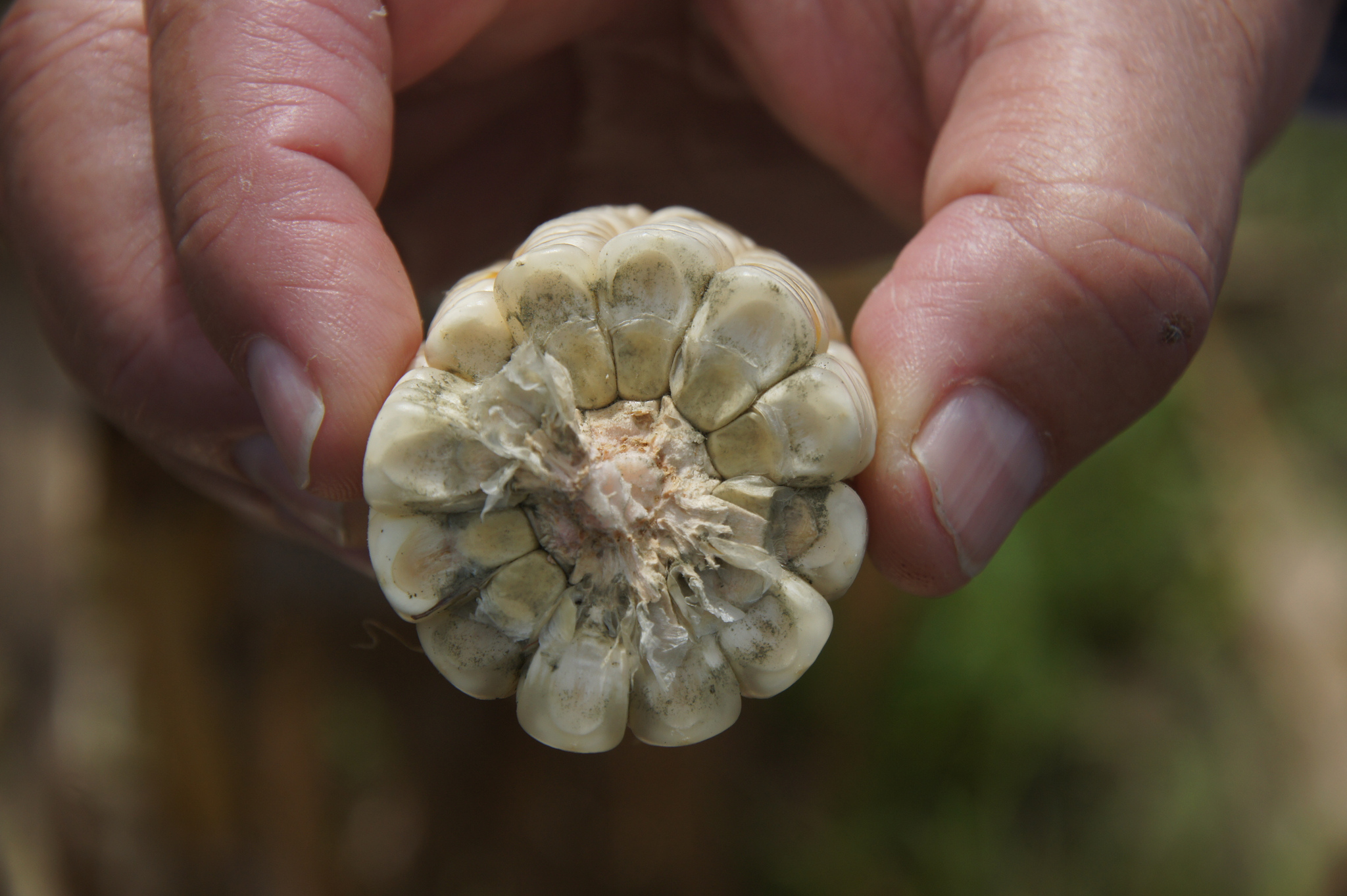
New publications: Biofortification of maize with provitamin A can reduce aflatoxin load
 Nutrition, health and food security
Nutrition, health and food security
This research is especially significant for countries where the health burdens of exposure to aflatoxin and prevalence of vitamin A deficiency converge with high rates of maize consumption.