An international team of scientists is working with farmers in the Yaqui Valley, in Mexico’s Sonora state, to develop and test a new mobile technology that aims to improve wheat and sugarcane productivity by helping farmers manage factors that cause the yield gap between crop potential and actual field performance.
Scientists have been developing and testing a smartphone app where farmers can record their farming activities — including sowing date, crop type and irrigation — and receive local, precise crop management advice in return.
This project is a private-public partnership known as Mexican COMPASS, or Mexican Crop Observation, Management & Production Analysis Services System.
Research has shown that proper timing of irrigation is more important to yields than total water amounts. Earlier planting times have also been shown to improve wheat yields. Having optimum dates for both activities could help farmers improve yields and stabilize their incomes.
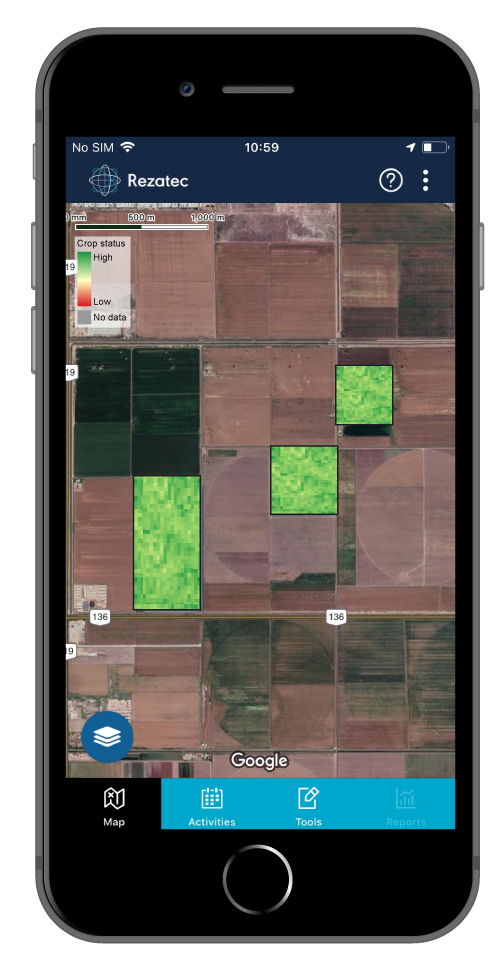
The COMPASS smartphone app uses earth observation satellite data and in-situ field data captured by farmers to provide information such as optimum sowing date and irrigation scheduling.
“Sowing and irrigation timing are well known drivers of yield potential in that region — these are two features of the app we’re about to validate during this next season,” explained Francelino Rodrigues, Precision Agriculture Scientist at the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT).
Sound data
Technological innovation for crop productivity is needed now more than ever with threats to food security increasing and natural resources becoming scarcer. Farmers are under increasing pressure to produce more with less, which means greater precision is needed in their agricultural practices.
The Yaqui Valley, Mexico’s biggest wheat producing area, is located in the semi-arid Sonoran Desert in the northern part of Mexico. Water security is a serious challenge and farmers must be very precise in their irrigation management.
The Mexican COMPASS consortium, which is made up of the geospatial data analytics company Rezatec, the University of Nottingham, Booker Tate, CIMMYT and the Colegio de Postgraduados (COLPOS) in Mexico, evolved as a way to help Mexican farmers improve their water use efficiency.
“Yaqui Valley farmers are very experienced farmers, however they can also benefit by using an app that is designed locally to inform and record their decisions,” Rodrigues explained.
The smartphone app will also allow farmers to record and schedule their crop management practices and will give them access to weekly time-series Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) maps, that will allow farmers to view their fields at any time from any location.
“All of this information is provided for free! That’s the exciting part of the project. The business model was designed so that farmers will not need to pay for access to the app and its features, in exchange for providing their crop field data. It’s a win-win situation,” said Rodrigues.
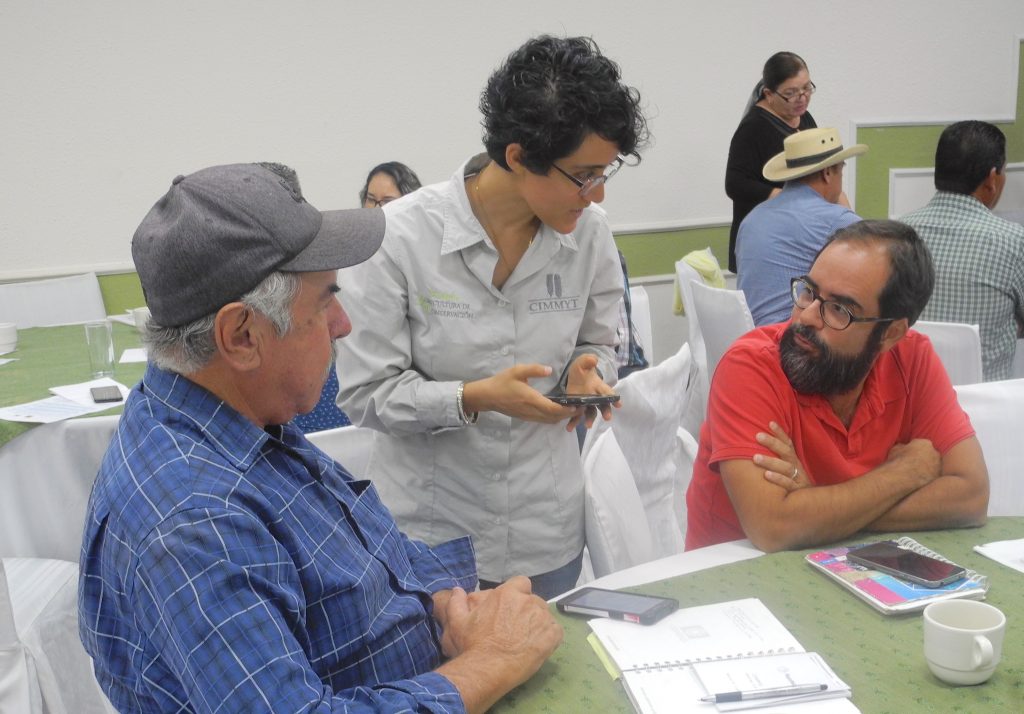

Farmer-centered design
The app is now in the validation stage and COMPASS partners are inviting farmers to test the technology on their own farms. A workshop on October 21 in Ciudad Obregon provided farmers with hands-on training for the app and allowed them to give their feedback.
Over 100 farmers attended the workshop, which featured presentations from Saravana Gurusamy, project manager at Rezatec, Iván Ortíz-Monasterio, principal scientist at CIMMYT, and representatives from local farmer groups Asociación de Organismos de Agricultores del Sur de Sonora (AOASS) and Distrito de Riego del Río Yaqui (DRRYAQUI). The workshop featured a step-by-step demonstration of the app and practical exercises for farmers to test it out for themselves.
“We need technology nowadays because we have to deal with many factors. The profit we get for wheat is getting smaller and smaller each year, so we have to be very productive. I hope that this app can help me to produce a better crop,” said one local wheat farmer who attended the workshop.
User feedback has played a key role in the development of the app. COMPASS interviewed dozens of farmers to see what design worked for them.
“Initially we came up with a really complicated design. However, when we gave it to farmers, they didn’t know how to use it,” explained Rezatec project manager, Saravana Gurusamy. The team went back to the drawing board and with the feedback they received from farmers, came up with a simple design that any farmer, regardless of their experience with technology or digital literacy, could use.
A farmer who attended the workshop talks about his experience and the potential benefits of the app. See full video on YouTube.
Sitting down with Gurusamy after the workshop, he outlined his vision for the future of the app.
“My vision is to see all the farmers in Sonora, working in wheat using the app. The first step is to prove the technology here, then roll it out to all of Mexico and eventually internationally.”
Mexican COMPASS is a four year project funded by the UK Space Agency’s International Partnership Programme (IPP-UKSA) and the CGIAR Research Program on Wheat (WHEAT). It is a collaboration between Rezatec, the University of Nottingham and Booker Tate in the UK, and the International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT) and the Colegio de Postgraduados (COLPOS) in Mexico.

 Innovations
Innovations 


