COVID-19 didn’t slow us down! In 2020, our editors continued to cover exciting news and events related to maize and wheat science around the world. Altogether, we published more than 250 stories.
It is impossible to capture all of the places and topics we reported on, but here are some highlights and our favorite stories of the year.
Thank you for being a loyal reader of CIMMYT’s news and features. We are already working on new stories and campaigns for 2021. Sign up for our newsletter and be the first to know!
The cereals imperative of future food systems
The 2019 EAT-Lancet Commission report defines specific actions to achieve a “planetary health diet” enhancing human nutrition and keeping resource use of food systems within planetary boundaries. With major cereals still supplying about one-third of calories required in the proposed diet, the way they are produced, processed, and consumed must be a central focus of global efforts to transform food systems. This article from our annual report argues three main reasons for this imperative.

Explainer: What is conservation agriculture?
Farmers are increasingly adopting conservation agriculture practices. This sustainable farming method is based on three principles: crop diversification, minimal soil movement and permanent soil cover.

Massive-scale genomic study reveals wheat diversity for crop improvement
A team of scientists has completed one of the largest genetic analyses ever done of any agricultural crop to find desirable traits in wheat’s extensive and unexplored diversity.

Reaching women with improved maize and wheat
The new AGG project aims to respond to the climate emergency and gender nexus through gender-intentional product profiles for its improved seed varieties and gender-intentional seed delivery pathways.
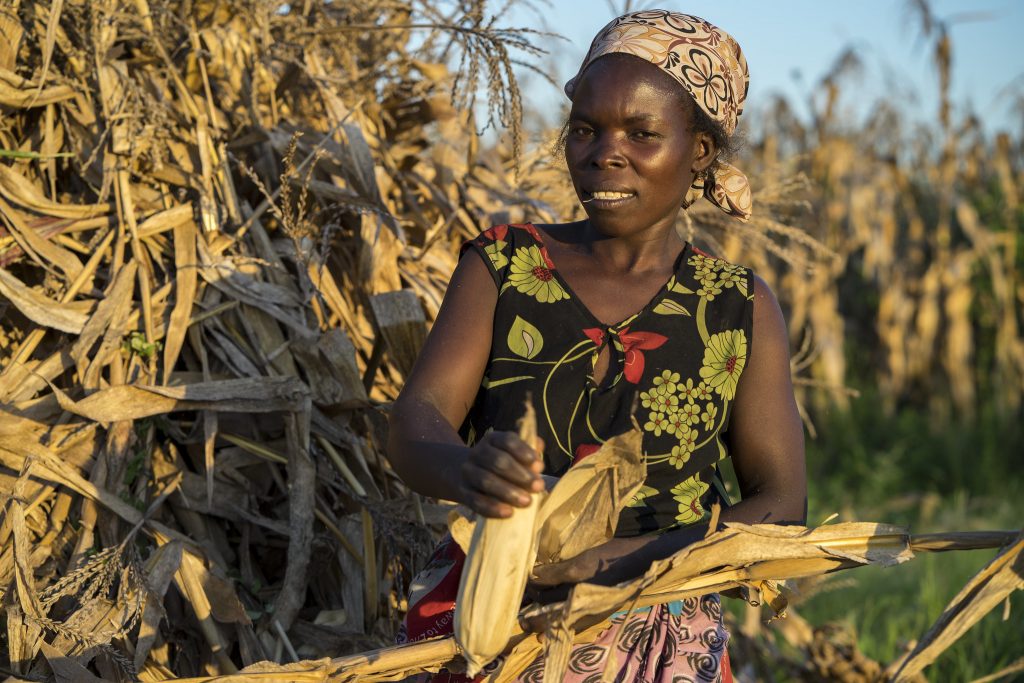

Safeguarding biodiversity is essential to prevent the next COVID-19
Experts share their insights on the link between biodiversity loss and emerging infectious diseases.

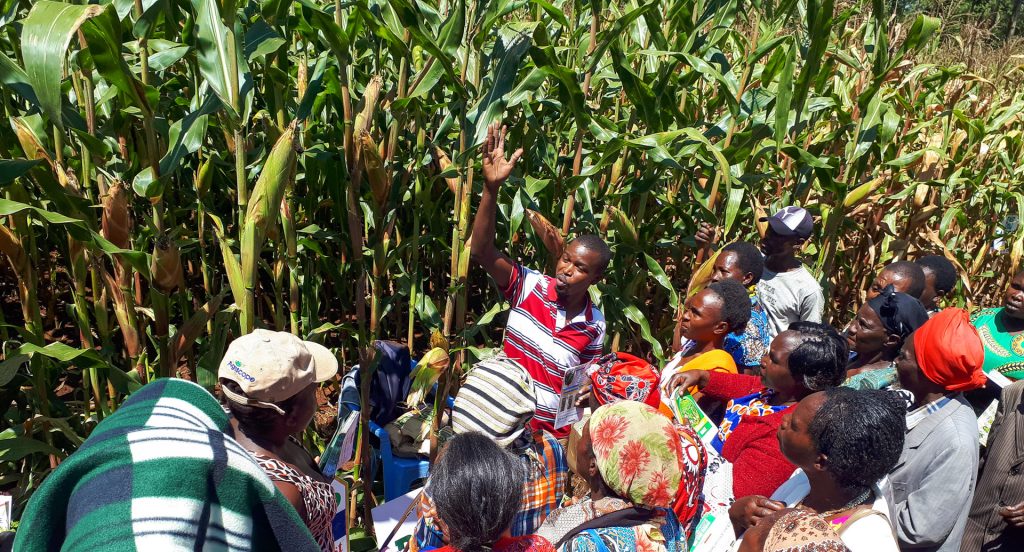
Seeing is believing
At demonstration farms, Kenyan farmers discover the stress-tolerant maize varieties they were looking for.

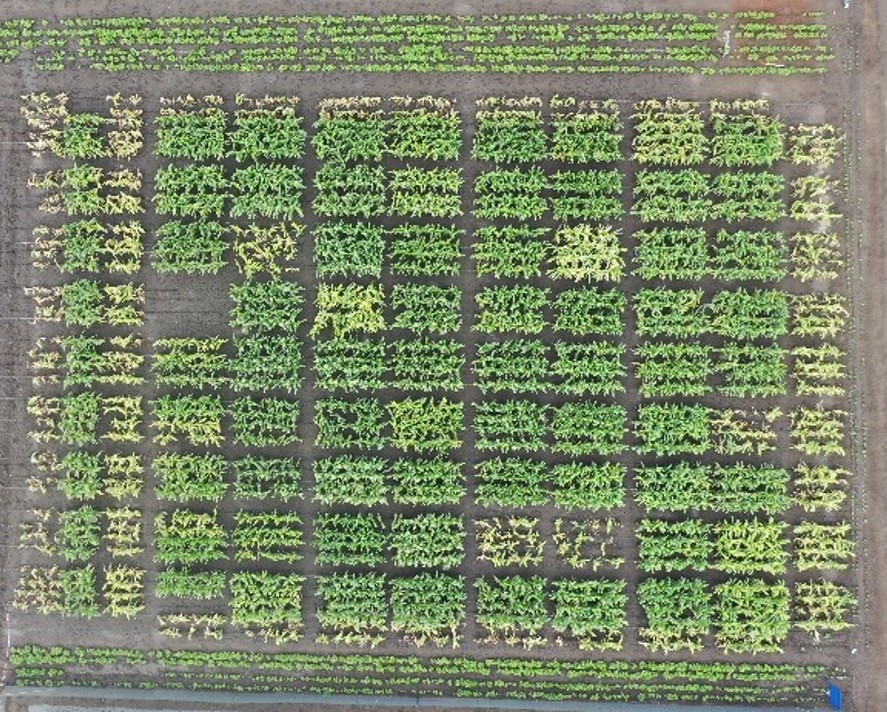
Battling devastating viral diseases, also in plants
Maize lethal necrosis (MLN) has taught us that intensive efforts to keep human and plant diseases at bay need to continue beyond the COVID-19 crisis. We interviewed B.M. Prasanna, director of the Global Maize Program at CIMMYT and the CGIAR Research Program on Maize (MAIZE), to discuss the MLN success story, the global COVID-19 crisis, and the similarities in the challenge to tackle plant and human viral diseases.
We had a similar conversation with Hans Braun, Director of the Global Wheat Program and the CGIAR Research Program on Wheat, who taled to us about the need for increased investment in crop disease research as the world risks a food security crisis related to COVID-19.

The many colors of maize, the material of life
The use of corn husk as veneer has helped a town to preserve maize biodiversity, protect the environment and reduce migration.

COVID-19 induced economic loss and ensuring food security for vulnerable groups
Study quantifies the economic losses from Bangladesh’s COVID-19 lockdowns and outlines policy implications for the country.
CIMMYT also published a similar study gauging the impact of COVID-19 lockdowns in Nepal.

Small is beautiful
Seven ways to make small-scale mechanization work for African farmers.

Cover photo: A member of a women farmers group serves a platter of mung bean dishes in Suklaphanta, Nepal. (Photo: Merit Maharajan/Amuse Communication)

 Innovations
Innovations