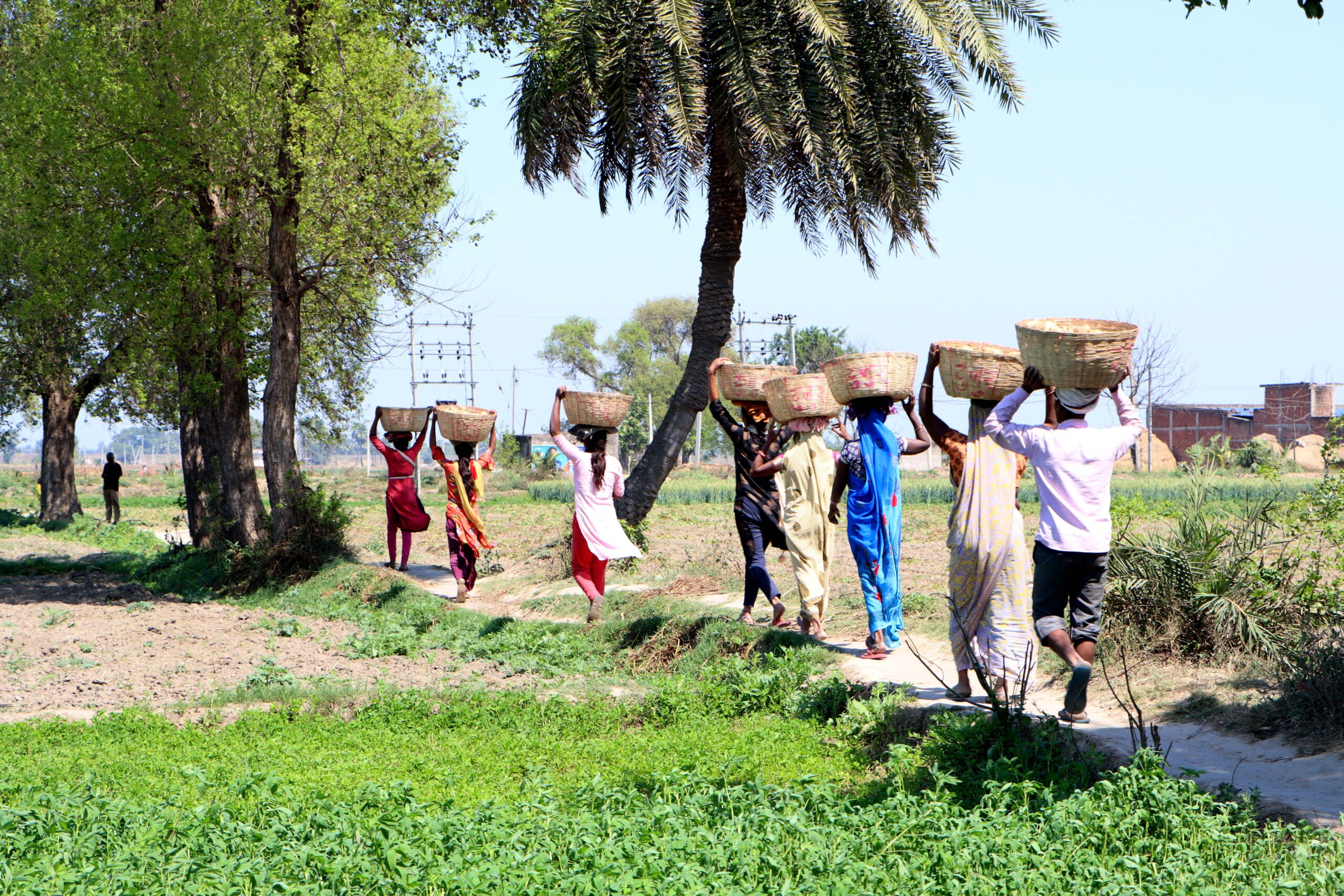

Bihar’s economy is driven by agriculture, which employs more than half of the workforce. With a yield of 27,654 kg per hectare from 330,000 hectares of land, Bihar accounts for 17% of India’s total potato production, behind only Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal. But the agricultural land is fraught with challenges: small and marginal farmers, who on average own less than 2 hectares of land, account for 97% of the landholdings. This creates less-than-ideal conditions for productive agriculture.
In Bihar’s largest potato-producing belt, a plethora of challenges make farming unprofitable: bottlenecks in getting good quality seeds, unaffordability of pesticides and fertilizers, the prevalence of crop pests and diseases, poor market prices at harvest time, and inadequate knowledge of good agronomic practices—all lead to lower net returns. Nalanda’s farmers are finding ways to make farming more profitable, productive, sustainable, and rewarding.
If this does not happen, farming will soon cease to be a lucrative—or even viable—livelihood.
Rita Devi, a 47-year-old farmer from Bihar, is one of 103 innovative farmers demonstrating new ways to tackle agricultural challenges through the Small Farmers Large Fields (SFLF) project, implemented by Transforming Agrifood Systems in South Asia (TAFSSA) in partnership with the International Potato Center (CIP).
Rita Devi inherited an acre of land after her husband’s prolonged illness and demise during the COVID-19 pandemic three years ago.
But she can’t imagine a world in which farming is a sustainable livelihood for her or future generations. “It’s hard to see profits in agriculture,” she sighs. “As long as the land size is small, how can the profits increase? The profits remain tiny, too.” For small farmers like Rita Devi, who are financially precarious, farming is neither a lucrative livelihood nor an aspirational lifestyle.
Rita Devi saw a glimmer of hope in the form of the SFLF program when she saw some people touring the village in September 2022, talking about farming in a new light.
Aggregation as a solution to farmers’ woes
In the field, TAFSSA staff at the International Potato Center (CIP), with support from the NGO Jeevika, mobilized farmers to pilot the SFLF collective action farming model.
Under the SFLF model, participating farmers organize themselves into groups to increase their collective bargaining power.
They buy inputs and secure farm services collectively from providers and achieve significant savings through bulk purchases; they improve their production practices and use quality seeds. Ultimately, their crops receive a premium for quality and volume.
The TAFSSA team planned to spread knowledge about improved farming practices among farmers and then use their collective bargaining power to procure better resources and prices. They started the initiative with training sessions.
Rajiv Ranjan, TAFSSA’s field coordinator and a farmer, said, “Varietal knowledge of seeds and crops was inadequate among farmers. They had no idea about the new varieties or how the different varieties performed.”
The training sessions combined presentations and interactive discussions with farmers, using visual aids such as photos and diagrams to enhance understanding. Key topics included field and seed preparation, high-yielding and disease-resistant crop varieties, irrigation optimization, and precision fertilizer application. Farmers also learned about preventive and reactive approaches to weed and disease management, and post-harvest handling and storage techniques.
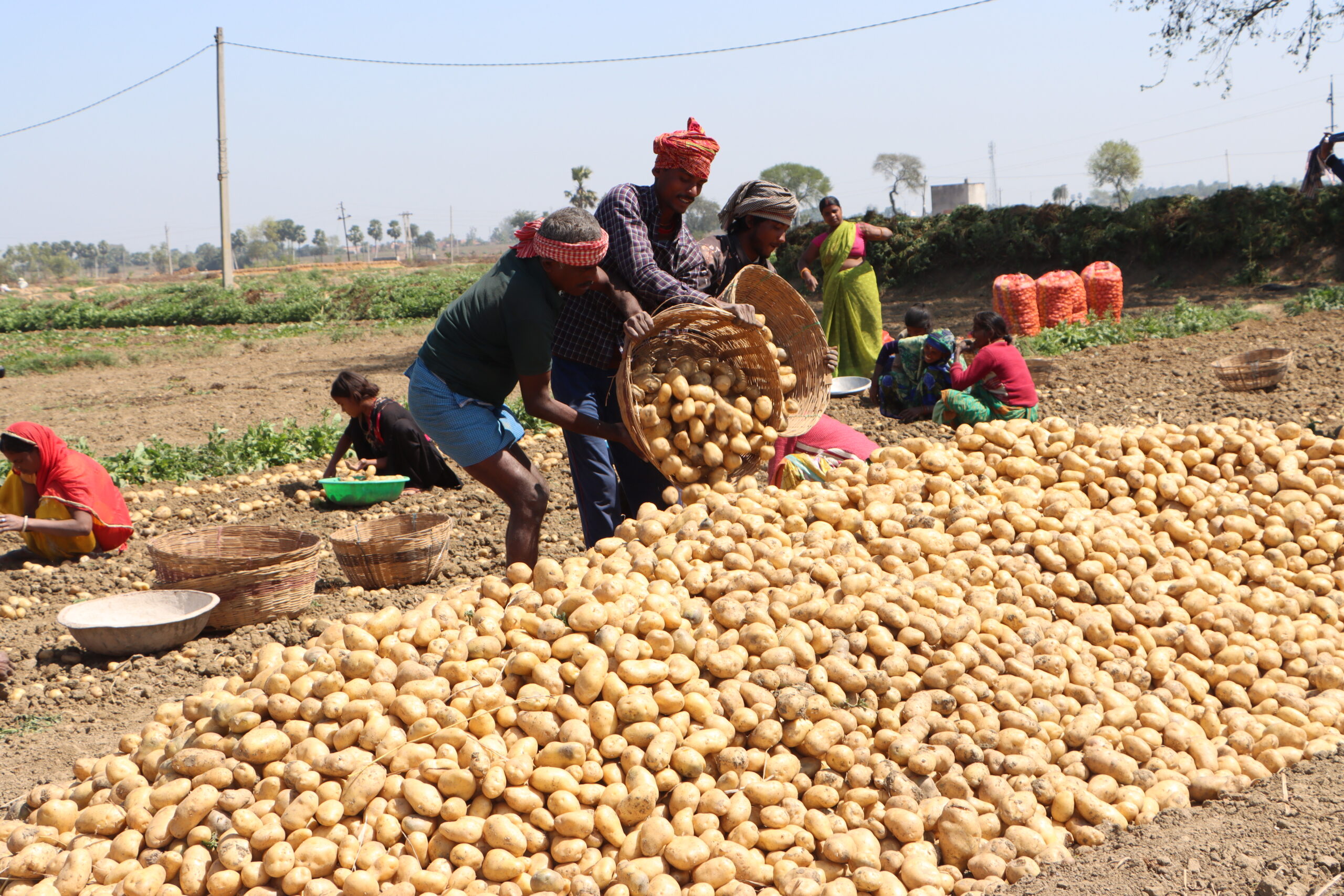

Connecting with farmers through the Small Farmers Large Fields pilot
Rita Devi decided to attend the training sessions in December 2022 to learn more about farming and explore how this new knowledge would help her reduce the costs of farming. Her main motivation was to improve her crop yield, which would be financially rewarding.
When TAFSSA staff first entered the villages and interacted with the farmers, many of them had their doubts about the interventions. International Potato Center (CIP) staff continued to meet with farmers in the villages and explain the benefits of collective farming. In the beginning, a few large farmers joined the program, and this led to the adoption of the practices by other small farmers. Trust was built over time.
The International Potato Center (CIP) developed a comprehensive Package of Practice (PoP) with illustrations of key field operations, major pests, and diseases. Accompanied by concise guidelines on input application methods, fertilizer and pesticide dosages, and timing during the crop cycle, the PoP was translated into Hindi, printed as a leaflet, and distributed to farmers in both pilot sites. Designed as a quick reference guide, the leaflet helps farmers with all aspects of potato and seed production, including efficient pest and disease identification and management.
Rita Devi recalls receiving information on water conservation, optimizing fertilizer dosage, and pest control, all of which led to monitored and restricted input use and financial savings.
“Now we know the correct amount of fertilizer dosage, and could save money,” said Rita Devi, who joined the pilot program in the rabi season of 2023–24 and implemented lessons she learned in the training and demonstrations. The financial savings were tangible and motivated her to move forward.
One of the lessons learned by her community is how to optimize irrigation for rabi potato, which requires five to six irrigation cycles in the region. The CIP team gave clear instructions on when these cycles should take place: first light irrigation 5–10 days after planting to cover one-third of the ridge, on-demand irrigation covering half of the ridge in subsequent cycles, stopping irrigation 8–10 days before harvest, and avoiding waterlogging at all times.
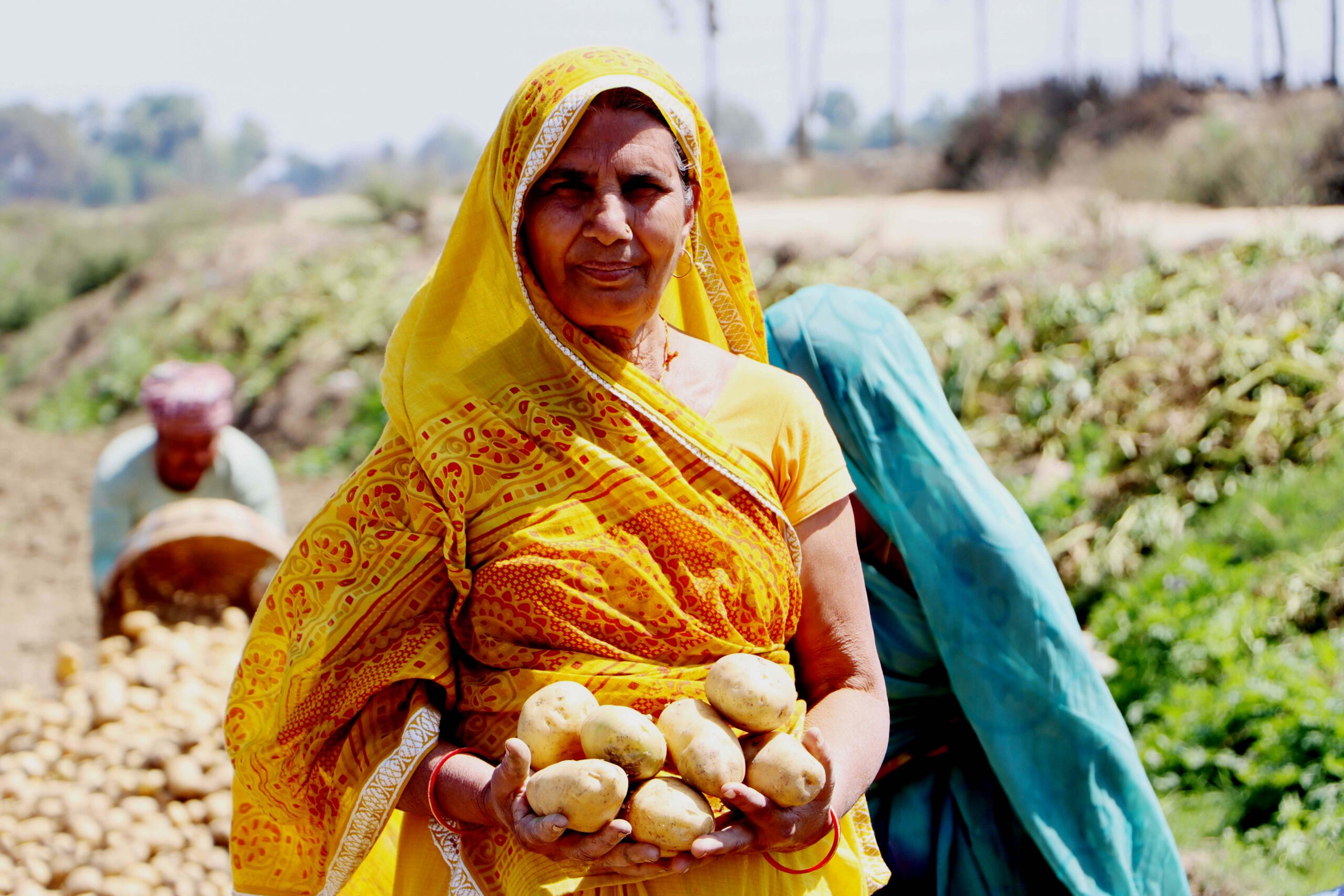

Harnessing collective strengths
The SFLF initiative aimed to strengthen farmers’ bargaining power by improving supply chain integration. A key focus was to help farmers collectively procure quality inputs such as seeds and fertilizers from reliable and affordable sources. High-quality seeds were sourced directly from Punjab, replacing expensive, substandard local options. Negotiated prices and proper storage ensured that farmers in Nalanda had seamless access to these resources. Similar arrangements were made for fertilizers and pesticides.
Rita Devi is a passionate supporter of the initiative for its financial and operational benefits. “Even if no one else makes the provision, we will form a farmer group to procure seeds from Punjab,” she asserts, reflecting the project’s effectiveness. Her determination shows how collective action and better linkages can empower smallholder farmers and optimize their farming practices.
In another exercise, Rita Devi tested crop diversification. After harvesting potatoes, she planted maize and moong beans on her farm to increase her farm income.
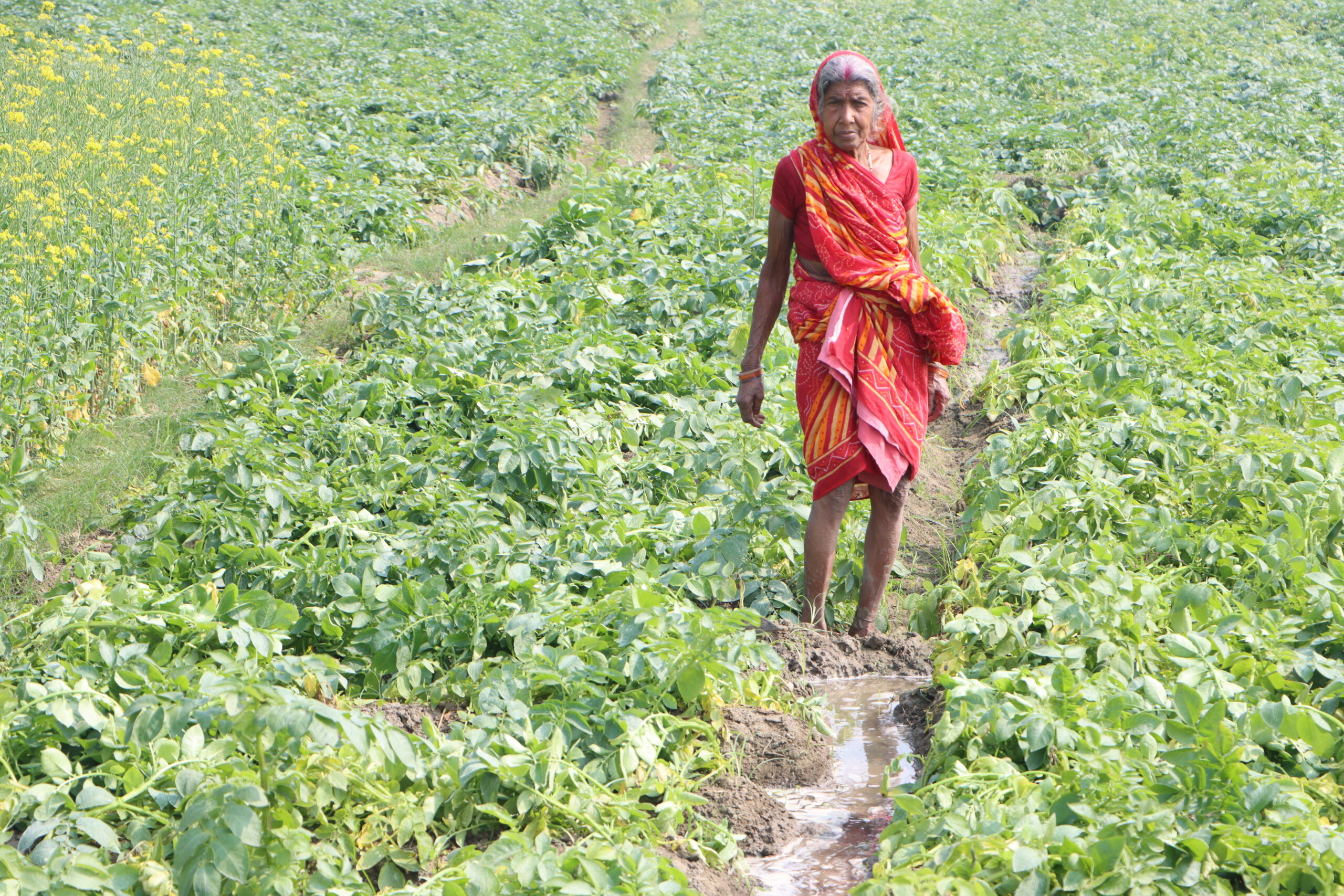

SFLF’s tangible and intangible impact
Ranjan attests to a noticeable change in farmers’ confidence: “SFLF has helped farmers by increasing knowledge and income. Information from local experts in the village and neighbouring villages also helped the farmers. Earlier, farmers were afraid of the quality of seeds they bought from the market. With the CIP linkages, they get assured quality and variety of seeds.”
With better seed quality and improved farming practices, Rita’s income from crops has improved. However, her profit is limited to the small plot. She is resourceful in her income generation: she plans to sell the surplus seed she has acquired to farmers during the rabi season in 2024.
Most farmers in the SFLF program have roughly doubled their incomes and net returns, after adjusting for production costs, compared to non-SFLF farmers.
Rita Devi hopes that as word spreads about the positive impact on yields and market values, more farmers will join the SFLF model. Additionally, subsequent seasons of the pilot will help refine the model to address all the prevalent issues they face.
 Innovations
Innovations